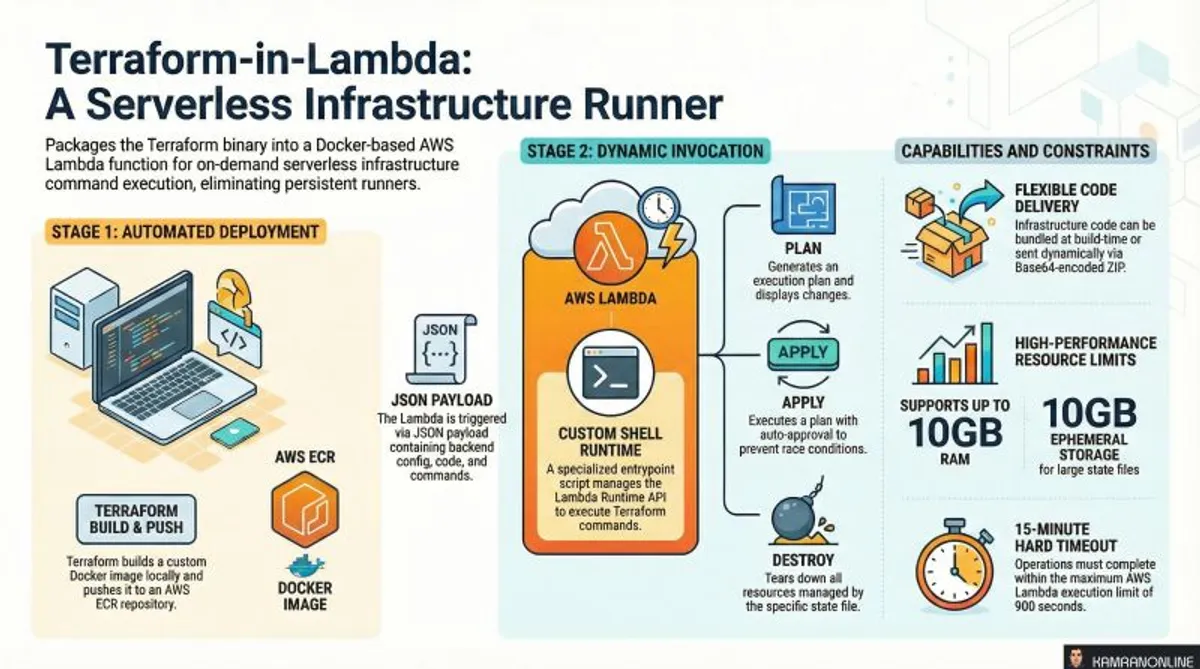
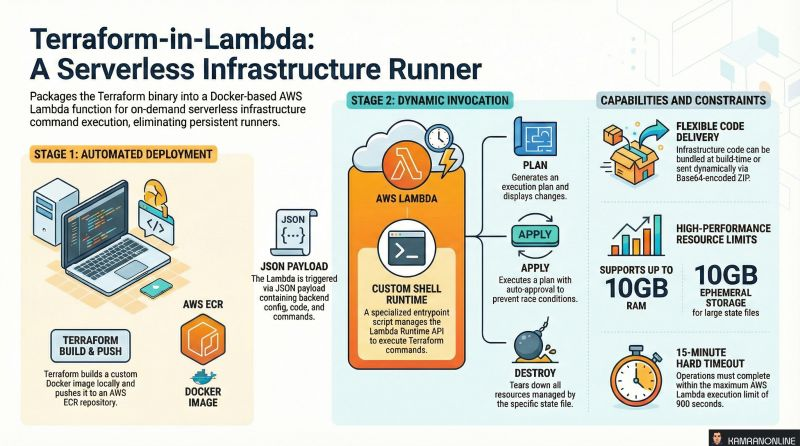
Terraform-in-Lambda: Building a Serverless Infrastructure Runner on AWS
- Kamran Biglari
- AWS , Terraform , Serverless , Automation
- 15 Feb, 2026
What if you could execute Terraform operations—plan, apply, destroy—without maintaining any infrastructure? No EC2 instances, no self-hosted runners, no dedicated CI/CD servers. Just pure, serverless, on-demand infrastructure automation.
I built terraform-in-lambda to do exactly that: a production-ready Terraform module that packages Terraform into an AWS Lambda function, turning it into a serverless infrastructure runner.
The Problem: Infrastructure Automation Overhead
Let’s talk about the typical Terraform execution patterns and their challenges:
Pattern 1: Developer Laptop
# Manual execution
cd infrastructure/
terraform plan
terraform applyProblems:
- ❌ No automation—requires manual intervention
- ❌ Inconsistent execution environments
- ❌ No audit trail or centralized logging
- ❌ Credential management scattered across developer machines
- ❌ Can’t respond to events (alarms, schedule, API calls)
Pattern 2: CI/CD Pipeline (GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins)
# GitHub Actions workflow
jobs:
terraform:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Terraform Apply
run: terraform apply -auto-approveProblems:
- ❌ CI/CD runners require persistent infrastructure (hosted or self-hosted)
- ❌ Self-hosted runners need maintenance, updates, and monitoring
- ❌ GitHub Actions minutes cost money at scale
- ❌ Difficult to trigger from AWS events (CloudWatch alarms, EventBridge)
- ❌ GitOps-only (can’t easily trigger programmatically)
Pattern 3: Dedicated EC2 Instance / Bastion
# SSH into bastion
ssh bastion.company.com
cd /infrastructure
terraform applyProblems:
- ❌ EC2 instance running 24/7 for occasional Terraform runs
- ❌ Requires patching, hardening, and monitoring
- ❌ Single point of failure
- ❌ Cost inefficient—paying for idle time
The Solution: Terraform as a Lambda Function
What if Terraform execution could be:
- ✅ Serverless — No infrastructure to maintain
- ✅ Event-driven — Triggered by EventBridge, API Gateway, SNS, or manual invocations
- ✅ Cost-effective — Pay only for execution time (millisecond billing)
- ✅ Scalable — Lambda auto-scales across concurrent executions
- ✅ Secure — IAM-based permissions with temporary credentials
- ✅ Auditable — Full CloudWatch logging and CloudTrail events
That’s exactly what this module provides.
How It Works: Architecture Deep-Dive
The module implements a Docker-based Lambda function with a custom shell runtime that executes Terraform commands on demand.
Build Phase: Creating the Lambda Container
Step 1: Docker Image Construction
The module builds a custom Docker image based on hashicorp/terraform:
FROM hashicorp/terraform:1.11-alpine
# Install dependencies
RUN apk add --no-cache \
aws-cli \
jq \
zip \
unzip \
curl \
bash \
dos2unix
# Copy custom runtime
COPY entrypoint.sh /entrypoint.sh
RUN chmod +x /entrypoint.sh
ENTRYPOINT ["/entrypoint.sh"]Why these dependencies?
aws-cli— Credential configuration and AWS operationsjq— JSON parsing for Lambda Runtime APIzip/unzip— Extract dynamically sent Terraform codecurl— Communicate with Lambda Runtime APIbash— Execute Terraform commandsdos2unix— Handle cross-platform line endings
Step 2: ECR Image Storage
The kreuzwerker/docker Terraform provider automatically:
- Builds the Docker image locally
- Authenticates to your ECR registry
- Pushes the image to ECR
- Tags with proper versioning
resource "docker_image" "terraform_lambda" {
name = "${aws_ecr_repository.this.repository_url}:${var.image_tag}"
build {
context = "${path.module}/docker"
dockerfile = "Dockerfile"
build_args = {
TERRAFORM_VERSION = var.terraform_version
}
}
}Step 3: Lambda Function Creation
resource "aws_lambda_function" "terraform_runner" {
function_name = var.function_name
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_exec.arn
package_type = "Image"
image_uri = docker_image.terraform_lambda.name
timeout = var.function_timeout # Up to 15 minutes
memory_size = var.function_memory_size # Up to 10GB
ephemeral_storage {
size = var.ephemeral_storage_size # Up to 10GB for /tmp
}
}Execution Phase: Custom Runtime Implementation
The magic happens in entrypoint.sh, which implements the Lambda Runtime API:
The Runtime Loop:
#!/bin/bash
set -euo pipefail
# Lambda Runtime API endpoints
RUNTIME_API="http://${AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_API}/2018-06-01/runtime"
while true; do
# 1. Poll for next invocation
HEADERS=$(mktemp)
EVENT_DATA=$(curl -sS -LD "$HEADERS" -X GET "${RUNTIME_API}/invocation/next")
# 2. Extract request ID from headers
REQUEST_ID=$(grep -Fi Lambda-Runtime-Aws-Request-Id "$HEADERS" | tr -d '[:space:]' | cut -d: -f2)
# 3. Parse event payload
COMMAND=$(echo "$EVENT_DATA" | jq -r '.command // "plan"')
TF_CODE=$(echo "$EVENT_DATA" | jq -r '.tf_code // ""')
BACKEND=$(echo "$EVENT_DATA" | jq -r '.backend // ""')
# 4. Configure AWS credentials (if provided)
if [[ -n "$(echo "$EVENT_DATA" | jq -r '.aws_access_key // ""')" ]]; then
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$(echo "$EVENT_DATA" | jq -r '.aws_access_key')
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$(echo "$EVENT_DATA" | jq -r '.aws_secret_key')
export AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=$(echo "$EVENT_DATA" | jq -r '.aws_session_token // ""')
fi
# 5. Extract Terraform code (if dynamic)
if [[ -n "$TF_CODE" ]]; then
echo "$TF_CODE" | base64 -d > /tmp/code.zip
unzip -o /tmp/code.zip -d /tmp/terraform
elif [[ -d /bundled-code ]]; then
cp -r /bundled-code /tmp/terraform
fi
# 6. Write backend configuration
if [[ -n "$BACKEND" ]]; then
echo "$BACKEND" | base64 -d > /tmp/terraform/backend.tf
fi
# 7. Execute Terraform
cd /tmp/terraform
terraform init -input=false
terraform $COMMAND -input=false -auto-approve
# 8. Report success
curl -X POST "${RUNTIME_API}/invocation/${REQUEST_ID}/response" -d '{"status":"success"}'
doneKey Design Decisions:
- Infinite Loop: Lambda keeps the container alive for subsequent invocations (warm starts)
- Runtime API Contract: Implements the standard AWS Lambda interface without language-specific SDKs
- Dynamic Code Loading: Supports both bundled code (fast) and runtime code (flexible)
- Credential Flexibility: Uses Lambda role by default, allows override for multi-account scenarios
- Ephemeral Filesystem: Uses
/tmp(up to 10GB) for Terraform working directory
Capabilities and Constraints
What You Can Do
✅ Terraform Commands:
plan— Preview infrastructure changesapply— Create/update infrastructuredestroy— Tear down resourcesvalidate— Check configuration syntaxinit— Initialize backend (usually automatic)
✅ Flexible Code Delivery:
Option 1: Bundle at Build Time (Faster)
module "terraform_lambda" {
source = "KamranBiglari/terraform-in-lambda/aws"
terraform_code_source_path = "${path.module}/infrastructure"
terraform_code_source_exclude = [
".terraform/**",
"*.tfstate*"
]
}Option 2: Send Code Dynamically (More Flexible)
{
"command": "apply",
"tf_code": "<base64-encoded-zip-of-terraform-files>",
"backend": "<base64-encoded-backend-config>"
}✅ Custom Environment Variables:
{
"command": "apply",
"envs": "VEZfVkFSX3JlZ2lvbj11cy1lYXN0LTEKVEZfVkFSX2Vudmlyb25tZW50PXByb2Q="
}Decodes to:
TF_VAR_region=us-east-1
TF_VAR_environment=prod✅ Multi-Account Execution:
{
"command": "apply",
"aws_access_key": "AKIA...",
"aws_secret_key": "...",
"aws_session_token": "..."
}✅ Private Terraform Registry:
{
"command": "plan",
"tfconfig": "ewogICJjcmVkZW50aWFscyI6IHsKICAgICJhcHAudGVycmFmb3JtLmlvIjogewogICAgICAidG9rZW4iOiAiLi4uIgogICAgfQogIH0KfQo="
}Constraints
⏱️ 15-Minute Timeout:
- Lambda maximum execution time is 900 seconds
- Large infrastructure operations may exceed this limit
- Solution: Break into smaller operations or use Step Functions for orchestration
💾 10GB Ephemeral Storage:
/tmpfilesystem limited to 10GB- Large Terraform states or provider downloads may hit limits
- Solution: Use remote state (S3), minimize provider cache
🔐 Secrets in CloudWatch Logs:
- Terraform output (including sensitive values) goes to CloudWatch
- Solution: Mark outputs as
sensitive = truein Terraform, use encryption at rest for logs
🐳 Build-Time Dependency:
- Requires Docker Engine on deployment machine
- Solution: Run Terraform deployments from CI/CD or local development machines with Docker
Implementation Guide
Prerequisites
1. Local Requirements:
- Docker Engine running (for image builds)
- Terraform >= 1.0.11
- AWS credentials configured
2. AWS Requirements:
- ECR repository (created automatically)
- IAM permissions for Lambda, ECR, CloudWatch
- Optional: VPC for network-isolated execution
Step 1: Deploy the Module
Create a main.tf:
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 5.8"
}
docker = {
source = "kreuzwerker/docker"
version = "~> 3.0"
}
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1"
}
# Docker provider for building images
provider "docker" {
registry_auth {
address = data.aws_ecr_authorization_token.token.proxy_endpoint
username = data.aws_ecr_authorization_token.token.user_name
password = data.aws_ecr_authorization_token.token.password
}
}
data "aws_ecr_authorization_token" "token" {}
module "terraform_lambda" {
source = "KamranBiglari/terraform-in-lambda/aws"
version = "1.0.0"
# Basic Configuration
function_name = "terraform-runner"
terraform_version = "1.11"
# Resource Allocation
function_timeout = 900 # 15 minutes
function_memory_size = 4096 # 4GB
ephemeral_storage_size = 4096 # 4GB
# Optional: Bundle Terraform code at build time
terraform_code_source_path = "${path.module}/infrastructure"
terraform_code_source_exclude = [
".terraform/**",
"*.tfstate*",
".git/**"
]
# Optional: VPC deployment
function_create_sg = false
function_vpc_subnet_ids = []
# CloudWatch Logs
function_cloudwatch_logs_retention_in_days = 30
tags = {
Environment = "production"
ManagedBy = "terraform"
}
}
output "lambda_function_name" {
value = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_function_name
}
output "lambda_function_arn" {
value = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_function_arn
}Deploy:
terraform init
terraform applyWhat gets created:
- ECR repository for Docker images
- Docker image built and pushed to ECR
- Lambda function with IAM execution role
- CloudWatch log group
- Optional: VPC security group
Step 2: Create IAM Policies for Terraform Execution
The Lambda needs permissions to manage infrastructure. Create a custom policy:
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "terraform_permissions" {
name = "terraform-execution-permissions"
role = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_execution_role_id
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"ec2:*",
"s3:*",
"dynamodb:*",
"iam:*",
# Add all AWS services your Terraform code manages
]
Resource = "*"
}
]
})
}Security Best Practice: Grant least-privilege permissions based on what your Terraform code actually manages.
Step 3: Invoke the Lambda Function
Option A: AWS CLI (Testing)
# Execute a Terraform plan with bundled code
aws lambda invoke \
--function-name terraform-runner \
--payload '{"command": "plan"}' \
response.json
cat response.jsonOption B: With Dynamic Code
# Prepare Terraform code
cd infrastructure/
zip -r /tmp/code.zip *.tf
# Base64 encode
TF_CODE=$(base64 -w 0 /tmp/code.zip)
# Backend configuration
BACKEND_CONFIG='
terraform {
backend "s3" {
bucket = "my-terraform-state"
key = "prod/infrastructure.tfstate"
region = "us-east-1"
}
}
'
BACKEND=$(echo "$BACKEND_CONFIG" | base64 -w 0)
# Invoke
aws lambda invoke \
--function-name terraform-runner \
--payload "{
\"command\": \"apply\",
\"tf_code\": \"$TF_CODE\",
\"backend\": \"$BACKEND\"
}" \
response.jsonOption C: From Python Application
import boto3
import base64
import json
lambda_client = boto3.client('lambda')
# Prepare Terraform code
with open('/tmp/code.zip', 'rb') as f:
tf_code_b64 = base64.b64encode(f.read()).decode()
# Prepare backend config
backend_config = """
terraform {
backend "s3" {
bucket = "my-terraform-state"
key = "prod/infrastructure.tfstate"
region = "us-east-1"
}
}
"""
backend_b64 = base64.b64encode(backend_config.encode()).decode()
# Invoke
response = lambda_client.invoke(
FunctionName='terraform-runner',
InvocationType='RequestResponse',
Payload=json.dumps({
'command': 'apply',
'tf_code': tf_code_b64,
'backend': backend_b64
})
)
result = json.loads(response['Payload'].read())
print(result)Real-World Use Cases
1. Scheduled Drift Detection and Remediation
Automatically detect and fix configuration drift every night:
# EventBridge rule
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_rule" "nightly_drift_check" {
name = "nightly-terraform-reconciliation"
schedule_expression = "cron(0 2 * * ? *)" # 2 AM daily
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_target" "lambda" {
rule = aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.nightly_drift_check.name
target_id = "terraform-runner"
arn = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_function_arn
input = jsonencode({
command = "apply"
# Code bundled in Lambda container
})
}
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "allow_eventbridge" {
statement_id = "AllowExecutionFromEventBridge"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_function_name
principal = "events.amazonaws.com"
source_arn = aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.nightly_drift_check.arn
}Result: Infrastructure stays compliant 24/7 without manual intervention.
2. Self-Service Developer Platform
Build an internal platform where developers request infrastructure via API:
# Flask API endpoint
@app.route('/infrastructure/create', methods=['POST'])
def create_infrastructure():
data = request.json
# Generate Terraform code from template
tf_code = render_template('vpc.tf.j2',
region=data['region'],
cidr=data['cidr_block'],
environment=data['environment']
)
# Zip and encode
zip_buffer = create_zip({'main.tf': tf_code})
tf_code_b64 = base64.b64encode(zip_buffer.getvalue()).decode()
# Invoke Lambda
lambda_client.invoke(
FunctionName='terraform-runner',
InvocationType='Event', # Async
Payload=json.dumps({
'command': 'apply',
'tf_code': tf_code_b64,
'backend': generate_backend_config(data['project_id'])
})
)
return {'status': 'provisioning', 'job_id': '...'}Result: Developers get infrastructure on-demand without Terraform knowledge.
3. Event-Driven Infrastructure Scaling
Respond to CloudWatch alarms by provisioning additional resources:
# CloudWatch Alarm → SNS → Lambda
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "high_cpu" {
alarm_name = "rds-high-cpu"
comparison_operator = "GreaterThanThreshold"
evaluation_periods = 2
metric_name = "CPUUtilization"
namespace = "AWS/RDS"
period = 300
statistic = "Average"
threshold = 80
alarm_actions = [aws_sns_topic.scaling.arn]
}
resource "aws_sns_topic_subscription" "lambda" {
topic_arn = aws_sns_topic.scaling.arn
protocol = "lambda"
endpoint = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_function_arn
}Lambda payload handler:
# In entrypoint.sh - parse SNS message
ALARM_NAME=$(echo "$EVENT_DATA" | jq -r '.Records[0].Sns.Message' | jq -r '.AlarmName')
if [[ "$ALARM_NAME" == "rds-high-cpu" ]]; then
# Apply Terraform to add read replica
cd /tmp/terraform
terraform apply -var="add_replica=true" -auto-approve
fiResult: Infrastructure auto-scales based on metrics.
4. Multi-Account Infrastructure Management
Centralized infrastructure management across AWS accounts:
# Admin Lambda invokes Terraform for each account
accounts = [
{'id': '111111111111', 'role': 'arn:aws:iam::111111111111:role/TerraformRole'},
{'id': '222222222222', 'role': 'arn:aws:iam::222222222222:role/TerraformRole'},
]
for account in accounts:
# Assume role
sts = boto3.client('sts')
creds = sts.assume_role(
RoleArn=account['role'],
RoleSessionName='terraform-runner'
)
# Invoke Lambda with temporary credentials
lambda_client.invoke(
FunctionName='terraform-runner',
Payload=json.dumps({
'command': 'apply',
'aws_access_key': creds['Credentials']['AccessKeyId'],
'aws_secret_key': creds['Credentials']['SecretAccessKey'],
'aws_session_token': creds['Credentials']['SessionToken'],
'tf_code': get_account_terraform_code(account['id'])
})
)Result: Single Lambda manages infrastructure across organizational units.
5. Ephemeral Testing Environments
Spin up and tear down test environments on-demand:
# CI/CD pipeline
- name: Create Test Environment
run: |
aws lambda invoke \
--function-name terraform-runner \
--payload '{"command": "apply", "envs": "'$(echo "TF_VAR_branch=$BRANCH_NAME" | base64)'"}'
- name: Run Integration Tests
run: pytest tests/integration/
- name: Destroy Test Environment
run: |
aws lambda invoke \
--function-name terraform-runner \
--payload '{"command": "destroy"}'Result: Zero-cost test environments that exist only during test execution.
Advanced Configuration
VPC Deployment for Private Resources
If your Terraform manages resources in private subnets:
module "terraform_lambda" {
source = "KamranBiglari/terraform-in-lambda/aws"
# ... other config ...
# VPC Configuration
function_create_sg = true
function_vpc_subnet_ids = [
"subnet-abc123",
"subnet-def456"
]
# Lambda will automatically create security group
# with egress to 0.0.0.0/0 (for Terraform provider downloads)
}Use cases:
- Managing RDS databases in private subnets
- Provisioning resources in isolated VPCs
- Compliance requirements for network isolation
Custom Terraform CLI Configuration
For private Terraform registries or custom provider mirrors:
{
"command": "plan",
"tfconfig": "ewogICJjcmVkZW50aWFscyI6IHsKICAgICJhcHAudGVycmFmb3JtLmlvIjogewogICAgICAidG9rZW4iOiAiWU9VUl9UT0tFTiIKICAgIH0KICB9Cn0K"
}Decodes to .terraformrc:
credentials "app.terraform.io" {
token = "YOUR_TOKEN"
}Debug Mode
Enable verbose output for troubleshooting:
{
"command": "apply",
"debug": true
}This outputs:
- Full Terraform execution logs
- AWS SDK debug information
- Environment variables (sanitized)
- File system state
Security Best Practices
1. Least-Privilege IAM Policies
Anti-pattern:
# DON'T DO THIS
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "bad" {
policy = jsonencode({
Statement = [{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = "*"
Resource = "*"
}]
})
}Best practice:
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "good" {
policy = jsonencode({
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"ec2:Describe*",
"ec2:CreateTags",
"ec2:DeleteTags"
]
Resource = "*"
},
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"ec2:RunInstances",
"ec2:TerminateInstances"
]
Resource = "arn:aws:ec2:*:*:instance/*"
Condition = {
StringEquals = {
"aws:RequestedRegion": ["us-east-1", "eu-west-1"]
}
}
}
]
})
}2. Encrypt CloudWatch Logs
resource "aws_cloudwatch_log_group" "terraform_lambda" {
name = "/aws/lambda/terraform-runner"
retention_in_days = 30
kms_key_id = aws_kms_key.logs.arn
}
resource "aws_kms_key" "logs" {
description = "Encrypt Terraform Lambda logs"
policy = jsonencode({
Statement = [
{
Sid = "Enable CloudWatch Logs"
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = {
Service = "logs.amazonaws.com"
}
Action = [
"kms:Encrypt",
"kms:Decrypt",
"kms:ReEncrypt*",
"kms:GenerateDataKey*",
"kms:CreateGrant",
"kms:DescribeKey"
]
Resource = "*"
}
]
})
}3. Secure Terraform State
Never store state in Lambda:
# Always use remote backend
terraform {
backend "s3" {
bucket = "my-terraform-state"
key = "prod/infrastructure.tfstate"
region = "us-east-1"
encrypt = true
dynamodb_table = "terraform-locks"
kms_key_id = "arn:aws:kms:us-east-1:123456789012:key/..."
}
}4. Validate Payloads
Implement input validation in Lambda:
# In entrypoint.sh
ALLOWED_COMMANDS=("plan" "apply" "destroy" "validate")
if [[ ! " ${ALLOWED_COMMANDS[@]} " =~ " ${COMMAND} " ]]; then
echo "Invalid command: $COMMAND"
curl -X POST "${RUNTIME_API}/invocation/${REQUEST_ID}/error" \
-d '{"errorMessage":"Invalid Terraform command"}'
continue
fi5. Enable ECR Image Scanning
resource "aws_ecr_repository" "terraform_lambda" {
name = "terraform-runner"
image_tag_mutability = "MUTABLE"
image_scanning_configuration {
scan_on_push = true
}
}Review scan results:
aws ecr describe-image-scan-findings \
--repository-name terraform-runner \
--image-id imageTag=latestMonitoring and Observability
CloudWatch Metrics
Key metrics to monitor:
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "lambda_errors" {
alarm_name = "terraform-lambda-errors"
comparison_operator = "GreaterThanThreshold"
evaluation_periods = 1
metric_name = "Errors"
namespace = "AWS/Lambda"
period = 300
statistic = "Sum"
threshold = 0
alarm_actions = [aws_sns_topic.alerts.arn]
dimensions = {
FunctionName = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_function_name
}
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "lambda_duration" {
alarm_name = "terraform-lambda-timeout-risk"
comparison_operator = "GreaterThanThreshold"
evaluation_periods = 1
metric_name = "Duration"
namespace = "AWS/Lambda"
period = 300
statistic = "Maximum"
threshold = 800000 # 800 seconds (warn before 900s timeout)
alarm_actions = [aws_sns_topic.alerts.arn]
dimensions = {
FunctionName = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_function_name
}
}CloudWatch Insights Queries
Find all Terraform apply operations:
fields @timestamp, @message
| filter @message like /terraform apply/
| sort @timestamp desc
| limit 100Identify failures:
fields @timestamp, @message
| filter @message like /Error:/
| stats count() by bin(5m)Track resource changes:
fields @timestamp, @message
| parse @message /Plan: (?<add>\d+) to add, (?<change>\d+) to change, (?<destroy>\d+) to destroy/
| filter ispresent(add)X-Ray Tracing (Advanced)
Enable distributed tracing:
resource "aws_lambda_function" "terraform_runner" {
# ... other config ...
tracing_config {
mode = "Active"
}
}Add to IAM role:
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "xray" {
role = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_execution_role_id
policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AWSXRayDaemonWriteAccess"
}Cost Optimization
Pricing Breakdown
Lambda pricing (us-east-1):
- Requests: $0.20 per 1M requests
- Duration: $0.0000166667 per GB-second
- Ephemeral storage: $0.0000000309 per GB-second (over 512MB)
Example: Daily drift detection
Assumptions:
- 4GB memory
- 2-minute execution
- 1 execution per day
Monthly cost:
Requests: 30 × $0.20 / 1,000,000 = $0.000006
Duration: 30 × (4 GB × 120s) × $0.0000166667 = $0.24
Total: ~$0.24/monthCompare to:
- EC2 t3.medium (24/7): ~$30/month
- GitHub Actions (2000 minutes/month): $0 (free tier), then $0.008/minute
Optimization Strategies
1. Right-Size Memory Allocation
# Test with different memory sizes
for memory in 1024 2048 4096 8192; do
aws lambda update-function-configuration \
--function-name terraform-runner \
--memory-size $memory
# Run test and measure duration
time aws lambda invoke --function-name terraform-runner ...
done2. Use Bundled Code When Possible
Bundled code avoids base64 encoding/decoding overhead:
# Faster execution
terraform_code_source_path = "${path.module}/infrastructure"vs.
// Slower execution (dynamic code)
{
"tf_code": "<base64-zip>"
}3. Optimize Container Image Size
# Multi-stage build to reduce image size
FROM hashicorp/terraform:1.11-alpine AS terraform
FROM alpine:3.19
COPY --from=terraform /bin/terraform /bin/terraform
# ... install only necessary tools4. Leverage Lambda SnapStart (Future)
Currently not supported for container images, but monitor for updates.
Troubleshooting Guide
Problem: “Task timed out after 900.00 seconds”
Cause: Terraform operation exceeds 15-minute Lambda limit.
Solutions:
-
Break into smaller operations:
# Instead of applying entire infrastructure # Split into modules and apply separately -
Use Step Functions for orchestration:
resource "aws_sfn_state_machine" "terraform_pipeline" { definition = jsonencode({ StartAt = "Init" States = { Init = { Type = "Task" Resource = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_function_arn Next = "Plan" } Plan = { Type = "Task" Resource = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_function_arn Next = "Apply" } Apply = { Type = "Task" Resource = module.terraform_lambda.lambda_function_arn End = true } } }) } -
Optimize Terraform performance:
# Use -parallelism flag terraform apply -parallelism=20 # Reduce provider re-initialization # Use persistent backend config
Problem: “Failed to download provider”
Cause: Lambda can’t reach Terraform Registry or GitHub.
Solutions:
-
VPC NAT Gateway:
# Ensure Lambda has internet access via NAT function_vpc_subnet_ids = [aws_subnet.private_with_nat.id] -
VPC Endpoints:
resource "aws_vpc_endpoint" "s3" { vpc_id = var.vpc_id service_name = "com.amazonaws.${var.region}.s3" } -
Provider caching:
# In Terraform code terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "~> 5.0" } } } # Cache in container image at build time
Problem: “No space left on device”
Cause: Terraform state or provider cache exceeds ephemeral storage.
Solutions:
-
Increase ephemeral storage:
ephemeral_storage_size = 10240 # 10GB max -
Use remote state:
terraform { backend "s3" { # Don't store large state locally } } -
Clean up /tmp:
# In entrypoint.sh, before terraform execution rm -rf /tmp/terraform/.terraform/providers/*
Problem: “Error: Unsupported credential source”
Cause: Credential provider chain misconfiguration.
Solutions:
-
Check environment variables:
# In CloudWatch logs echo "AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: $AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID" echo "AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: ${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY:0:4}***" -
Verify IAM role trust:
aws sts get-caller-identity -
Use explicit credentials:
{ "command": "plan", "aws_access_key": "...", "aws_secret_key": "..." }
Comparison: Lambda vs. Traditional Runners
| Feature | Lambda (This Module) | EC2 Runner | GitHub Actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Serverless | Self-managed | Hosted/Self-hosted |
| Cost (light usage) | ~$0.24/month | ~$30/month | Free tier, then $0.008/min |
| Scaling | Automatic | Manual | Limited concurrency |
| Maintenance | Zero | Patching, updates | Self-hosted: patching |
| Event-driven | Native | Complex | Webhook-based |
| Max execution time | 15 minutes | Unlimited | 6 hours (self-hosted: unlimited) |
| Cold start | 1-3 seconds | None | Variable |
| Multi-account | Native (AssumeRole) | Complex | Requires secrets |
| Audit logging | CloudTrail + CW | Manual | GitHub audit log |
Limitations and Considerations
When NOT to Use This
❌ Very Large Infrastructure Operations
- Terraform applies taking > 15 minutes
- Alternative: Use EC2 spot instances or AWS Batch
❌ Interactive Workflows
- Operations requiring human approval mid-execution
- Alternative: Use Terraform Cloud or Atlantis
❌ Persistent Terraform Workspaces
- Need to maintain multiple workspaces with local state
- Alternative: Terraform Cloud workspaces
❌ Complex Provider Authentication
- Providers requiring complex OAuth flows or device codes
- Alternative: Pre-authenticate and inject tokens
When This Excels
✅ Scheduled reconciliation — Nightly drift detection ✅ Event-driven provisioning — React to CloudWatch alarms, SNS topics ✅ API-driven infrastructure — Self-service platforms ✅ Multi-account management — Centralized control across AWS Organizations ✅ Ephemeral environments — Short-lived test infrastructure ✅ Cost-sensitive workloads — Avoid 24/7 runner costs
Conclusion
Running Terraform in AWS Lambda represents a paradigm shift in infrastructure automation—from infrastructure-based (EC2, CI/CD runners) to serverless, event-driven execution.
Key Benefits Recap
✅ Zero Infrastructure: No servers, no maintenance, no patching ✅ Cost-Effective: Pay only for execution time (~$0.24/month for daily runs) ✅ Event-Driven: Native integration with EventBridge, SNS, API Gateway ✅ Scalable: Concurrent executions for multi-account management ✅ Secure: IAM-based permissions with CloudTrail audit logging ✅ Flexible: Bundle code or send dynamically, support for custom credentials
Getting Started
- Explore the module: github.com/KamranBiglari/terraform-aws-terraform-in-lambda
- Check Terraform Registry: registry.terraform.io/modules/KamranBiglari/terraform-in-lambda/aws
- Start with bundled code: Deploy with your infrastructure pre-packaged
- Add event triggers: Set up EventBridge rules for scheduled execution
- Scale to production: Implement monitoring, alerting, and multi-account patterns
What’s Next?
The module is open source and actively maintained. Potential future enhancements:
- Terraform Cloud/Enterprise integration
- Step Functions-based long-running operation support
- Built-in approval workflows
- Enhanced observability with structured logging
This module bridges the gap between traditional Terraform execution and serverless, event-driven infrastructure management. Whether you’re building a self-service platform, automating drift detection, or managing multi-account infrastructure, Terraform-in-Lambda provides the foundation for serverless Infrastructure as Code.
Resources:
- GitHub Repository: terraform-aws-terraform-in-lambda
- Terraform Registry: Official Module
- AWS Lambda Runtime API: Documentation
- Terraform Documentation: AWS Provider
Have you tried running Terraform serverlessly? What use cases are you considering? Share your thoughts or reach out on LinkedIn!